WDI’s Performance Measurement and Improvement team, together with Good Business Lab, will conduct an ex-post evaluation of TechnoServe business accelerator programs that have operated in Chile, Peru, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama since 2008. Using WhatsApp and phone interviews to collect data from program participants, we seek to estimate the sustainability of the programs’ impact on the entrepreneurs and their businesses.
WDI has been working with the Peruvian American Medical Society (PAMS) for several years to develop its gastrointestinal specialty services business into a financially sustainable undertaking and toposition it as a GI center of excellence. This year WDI completed the business plan and began considering options for purchasing and servicing of equipment.
Investing in women’s health is a critical component of their economic and social development. However, while country economies and health systems have advanced, under-served women in Latin America have not necessarily obtained access to critical healthcare services and products. Supported by the Linked Foundation, WDI conducted a 2019 landscaping study, of key needs and potential areas for investment in women’s health in Latin America. Focused on Colombia and Peru, this report provides a landscape to catalyze impact investment interest and capital to the most-needed areas of women’s health in Latin America.
This primer provides a comprehensive but non-technical overview of the distinct health information systems (HIS) that all together support health care delivery in low-resource settings. It opens with a historical account and landscape assessment and describes the urgent need to build a lean rigorous HIS that integrates these different components. Subsequent sections describe the individual systems that: i) track individual patient and health care provider information; ii) directly document care delivery; iii) provide public and population health data; iv) support facilities’ and community health workers’ administrative and financial functions; and v) coordinate logistics and health commodities supply chains. A separate section describes imported data, including “master data” and manufactured (e.g., “meta”) data. The primer closes with recommendations for principled HIS stewardship.

An information session for students interested in enrolling in BA685: Healthcare Delivery in Emerging Markets will be held at 5:30 p.m. on Monday, Oct. 28 at the Ross School of Business, Blau Hall Room 1210. The class is offered by Michigan Ross and is organized and primarily funded by WDI.
The class is comprised mostly of second-year MBA students, but is open to all graduate students. It provides students with on-the-ground experience in a foreign country while also contributing to the success of partner health clinics and hospitals. The class also is designed to increase participants’ international leadership capabilities and enhance their awareness of diverse business issues within the current global landscape. It is taught by WDI President Paul Clyde.
The course responds to the increasing need from future employers that managers have international business perspectives to augment their business and management knowledge. During the first part of the term, students learn about healthcare in emerging markets through lectures, guest speakers and case discussions. Students are then divided into five teams and prepared for visits to their selected country, traveling to those destinations in late February and early March.
Last year, student teams worked in Ethiopia, India, Kenya, Peru and Rwanda.
Studying for her master’s degree in public health, Alison Granger was interested in a course at the University of Michigan that would let her take the lessons from her textbooks and classroom lectures and put it into practice.
That’s why she enrolled in BA685: Healthcare Delivery in Emerging Markets, a course offered at the Ross School of Business.
“I was interested in getting a more in-the-field, global perspective on what I’ve learned so far in class,” said Granger, who traveled to Ethiopia for her project. “And I did with this class.”
The class is comprised mostly of MBA2 students, but also is open others pursuing other graduate degrees such as Granger. It’s designed to enhance participants’ international leadership capabilities, increase awareness of diverse business issues within the current global landscape, provide on-the-ground experience in a foreign country and contribute to the success of partner health clinics and hospitals. It is taught by WDI President Paul Clyde.
The course, organized and primarily funded by WDI with some financial support from Michigan Ross, responds to the increasing need for managers with international business perspectives to augment their business and management knowledge. During the first part of the term, students learned about healthcare in emerging markets through lectures, guest speakers and case discussions. Students were then divided into five teams and prepared for visits to their selected country, traveling to those destinations in late February and early March.
This year, student teams worked in Ethiopia, India, Kenya, Peru and Rwanda. All five teams presented recaps of their projects on April 22 at Michigan Ross.
Clyde said the travel-study course lets students combine what they learned in the classroom with hands-on experience in the field. It features a collaborative learning environment with faculty and students learning from each other in an action-based learning setting.
“Through this course teams of students from Ross, SPH and School of Information have provided our partner healthcare organizations value through analysis of their operations, customers and strategy,” Clyde said. “Through this experience, the students gain unusual insights into the opportunities and challenges of operating healthcare organizations in LMICs.”
Here is a recap of the BA685 projects:
More than 1 million infants die each year due to severe respiratory distress, with 99 percent of these deaths in low- to middle-income countries, according to the World Health Organization. Current noninvasive ventilators are expensive, require skilled operators, and fail during power outages that are common in emerging markets. AIM Tech developed NeoVent, a low-cost, low-tech, easy-to-use ventilator that is non-electric and has only one moving part. It also can be manufactured at scale for less than 1 percent the cost of conventional ventilators.
 AIM Tech wanted the BA685 student team to evaluate if AIM Tech should enter the Indian market and provide recommendations for a market entry strategy. The students visited Delhi,
AIM Tech wanted the BA685 student team to evaluate if AIM Tech should enter the Indian market and provide recommendations for a market entry strategy. The students visited Delhi,
Mumbai and Chennai, and interviewed and provided product demonstrations to 24 healthcare facilities, one government official, two manufacturers and one distributor. The students found that the Indian healthcare market shows a high-growth trajectory. The government’s focus on entrepreneurship, insurance, and neonatology also creates favorable climate and demand for NeoVent, while clinicians see the product as unique, necessary and value it at a higher-than-planned price, the students noted.
They recommended AIM Tech license NeoVent to a multinational corporation with an existing foothold in the Indian market. Another suggestion was to pilot NeoVent with a large hospital following FDA approval.
 The lack of reliable, local liquid oxygen suppliers in Ethiopia for hospitals makes it necessary to have an oxygen separator system on the grounds for the hospital EADG is building. EADG asked the BA 685 students to study two questions: should EADG’s future hospital build and operate a medical gas plant?: and, should EADG sell excess medical gas to area hospitals?
The lack of reliable, local liquid oxygen suppliers in Ethiopia for hospitals makes it necessary to have an oxygen separator system on the grounds for the hospital EADG is building. EADG asked the BA 685 students to study two questions: should EADG’s future hospital build and operate a medical gas plant?: and, should EADG sell excess medical gas to area hospitals?
Based on research and interviews with hospitals with its own medical gas plants on-site, the students’ findings showed that EADG would benefit from building its own facility and could learn from other hospitals that have done the same. On the question of whether to sell excess medical gas, the students’ research showed it would not be a good decision to do so. It is not profitable, the research found, and there is robust competition and several barriers to entry in the market. The students encouraged EADG to begin the bidding process soon to select equipment suppliers because the hospital is expected to open in 2021. They also suggested EADG monitor the medical gas market for any movement or changes in government policy that might make it more profitable to sell excess medical gas.
Timely and accurate data reports are vital to operations at rural health clinics. Electronic records have been implemented, but poor staffing and internet connection have made e-records ineffective. The Ihangane Project, in partnership with nurses from rural health centers, created E-Heza Digital Health Record to deliver more timely and accurate data to the Rwanda Ministry of Health. The ministry has requested that E-Heza be expanded throughout Rwanda to serve maternal child care.
 The BA 685 students project was to establish a framework for evaluating the efficiency of the current data reporting system and E-Heza in terms of timeliness, cost and data quality. To accomplish this, the students: analyzed the current lead time for data to move from point of care to the Ministry of Health; identified the cost of data reporting, including revenue loss; defined measurements to evaluate data accuracy; and developed framework to evaluate the efficiency of data reporting.
The BA 685 students project was to establish a framework for evaluating the efficiency of the current data reporting system and E-Heza in terms of timeliness, cost and data quality. To accomplish this, the students: analyzed the current lead time for data to move from point of care to the Ministry of Health; identified the cost of data reporting, including revenue loss; defined measurements to evaluate data accuracy; and developed framework to evaluate the efficiency of data reporting.
The students recommended a framework that evaluated efficiency in terms of timeliness, cost savings and data quality.
For next steps, the students recommended recording observational data for each process in the workflow, testing the framework for E-Heza and other health modules and exploring and quantifying the potential adverse effect due to poor data quality.
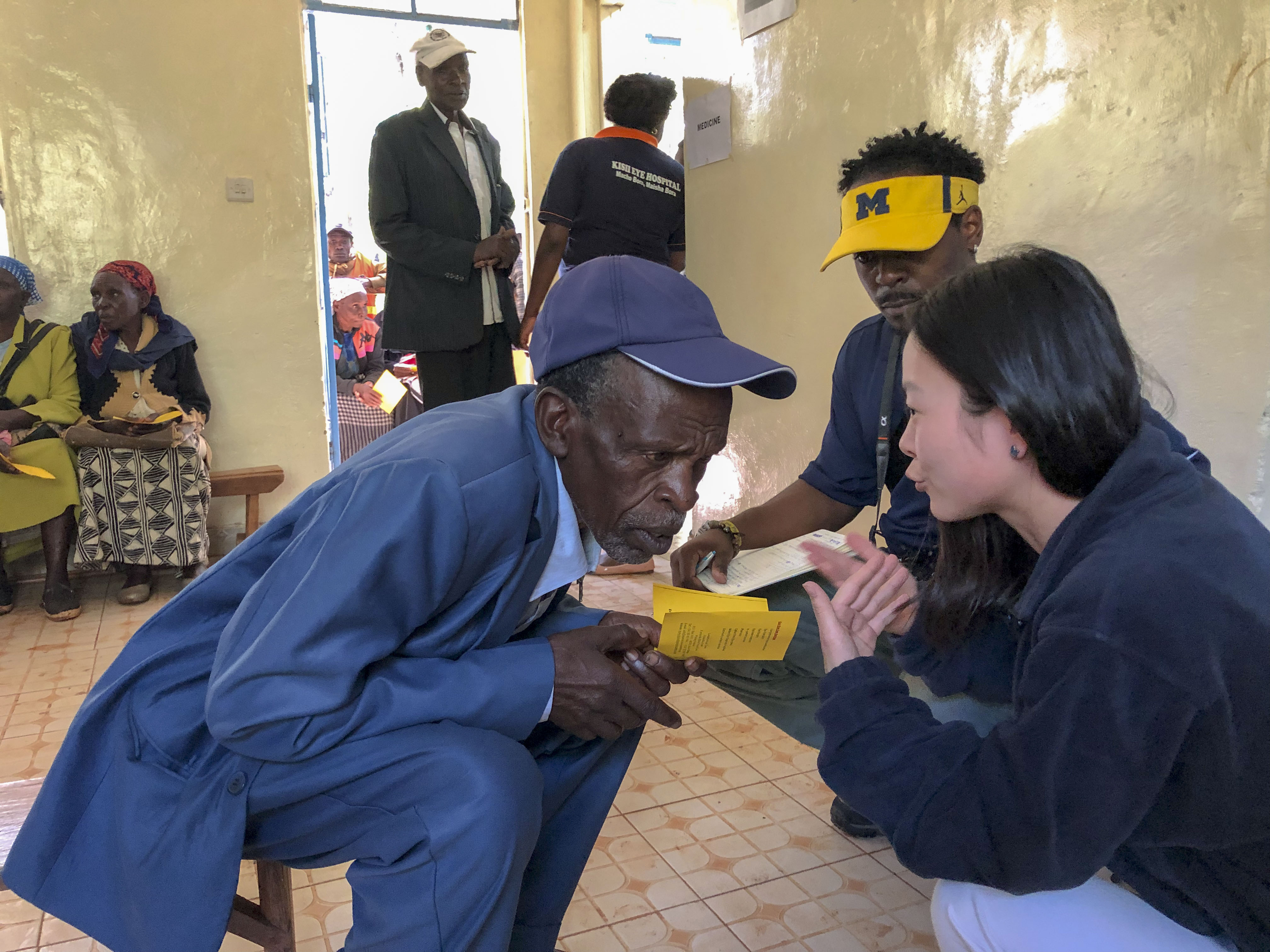
The Kisii Eye Care Institute started in 2013 and it has grown from an eye care service provider to a medical eye hospital and training center. It provides 3,000 surgeries annually but wants to increase the demand and capacity to 5,000 per year. Kisii operates as a social enterprise using an entrepreneurial approach to solve a social problem – avoidable blindness and visual impairment. Services are provided at normal rates for those who can afford them and substantially below cost to low-income members of their community.
 The BA685 student team put together a business plan for Kisii to increase demand for its services and improve operational efficiency. The students said surgery and optical services (glasses) are the largest revenue generators for Kisii and it must enhance its marketing strategy in both areas. Operationally, to decrease wait times and provide patients with a higher quality overall experience, current processes must be improved by standardizing the patient queue and improving counselor training, among other things. And to be ready for future growth, the current Kisii organizational structure must change, roles need to be redefined roles and responsibilities shifted.
The BA685 student team put together a business plan for Kisii to increase demand for its services and improve operational efficiency. The students said surgery and optical services (glasses) are the largest revenue generators for Kisii and it must enhance its marketing strategy in both areas. Operationally, to decrease wait times and provide patients with a higher quality overall experience, current processes must be improved by standardizing the patient queue and improving counselor training, among other things. And to be ready for future growth, the current Kisii organizational structure must change, roles need to be redefined roles and responsibilities shifted.
PAMS Policlinico wants to become a gastrointestinal (GI) center of excellence. It currently offers GI services and recently a GI doctor from the University of Michigan visited to develop an operational understanding.
 Last year’s BA685 team conducted a market analysis to determine how PAMS could grow to become a center of excellence in either GI or ophthalmology. This year’s student team built on that previous work and developed a complete business plan that: evaluated marketing strategy; studied GI equipment options to ensure there is an adequate plan for maintenance, repairs and acquisition; and, assessed opportunities to decouple skills and create a new position to take on some of the current physician duties. This business plan will be presented to potential PAMS funders this spring.
Last year’s BA685 team conducted a market analysis to determine how PAMS could grow to become a center of excellence in either GI or ophthalmology. This year’s student team built on that previous work and developed a complete business plan that: evaluated marketing strategy; studied GI equipment options to ensure there is an adequate plan for maintenance, repairs and acquisition; and, assessed opportunities to decouple skills and create a new position to take on some of the current physician duties. This business plan will be presented to potential PAMS funders this spring.
The students’ research and on-site observations and interviews showed: A lack of standardized practices lead to operational inefficiencies and lowered capacity even with sufficient personnel; contract incentives are not structured to achieve best outcome for PAMS; omission of certain accounting practice lowers visibility into financial health of PAMS and each specialties; and, the Polyclinic is one of the few providers of colonoscopies in the region.
The student team’s recommendations included: optimizing processes allowing for maximizing use of resources, including supplies and the time of healthcare providers; standardizing processes also decreases waste and allows more patients to be treated per week, ultimately increasing patient volume and with it, revenue.
PAMS in Chincha, Peru operates a primary care clinic that offers some specialty services. Since 2017, WDI has been working with the leadership to develop a business model that would enhance its gastroenterology services and turn it into a service that helps fund the rest of the clinic. Building on market analysis completed last year, this year recommendations on changes in operations and revenues were made. A business plan is in the final stages of completion and will be presented to potential funders.

Women working with Chakipi Acceso in Peru. Image courtesy of Chakipi.
Note: The following post was co-written by Rebecca Baylor, Heather Esper and Yaquta Kanchwala Fatehi of WDI’s Performance Measurement Initiative. It was originally published on NextBillion.net, which is managed by WDI.
For many businesses and organizations, the idea of measuring their impacts is usually one of three things: scary, elusive or just plain boring. To make matters worse, evaluators have a rotten reputation for using too much annoying technical jargon. While there is some truth to these stereotypes, it doesn’t have to be all bad.
Our work demonstrates that it is possible to bridge the gap between people and metrics in a meaningful way.
In fact, our team at the William Davidson Institute recently released an impact report that demonstrates how we guided three organizations on how to demystify data collection of their social impacts. We worked with senior level leadership to develop strong surveys and data collection processes suited to their context. Perhaps more importantly, we openly discussed their measurement concerns and made explicit– dare we say, energetic– connections between their impact metrics and organizational strategy.
A key theme throughout this project was our goal to combine social and business metrics. When organizations – from enterprises to impact investors – actually track these types of combinations, which we refer to as “power couples,” they can absorb unique insights to solve key business challenges while communicating impact evidence. Through our work, we have encountered a number of social + business metric power couples that we’ve seen influence internal decision-making at organizations and improve results. Creating these power couples enables managers to more holistically harness their data to better meet business goals and increase intended impacts. For example, employee retention, an all-important business metric, may be affected by the impact that an organization has on the quality of life of their employees’ children, a social metric. This may be especially true for low- or middle-income employees.
Here are just a few common power couples that we identified during this project (detailed in the report) and others.
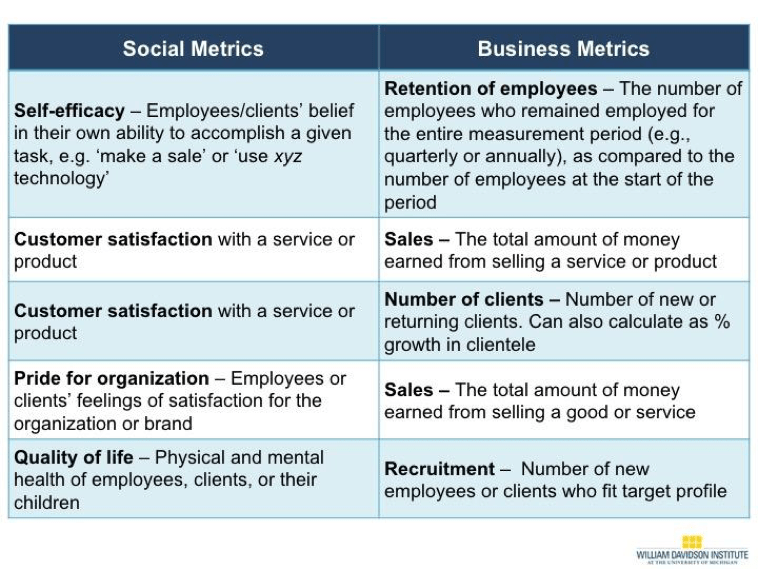
This list is just a start.
Selecting metrics takes time and patience. Indeed, finding the right metrics can be a lot like parenting. There isn’t one perfect formula and your strategy will likely evolve over time. However, we recommend businesses and investors interested in seeing social or environmental impact use some of the following strategies to make their job easier. We’re also including relevant resources to help you apply these strategies:
We hope these combinations excite you and inspire you to create a few social + business metrics of your own. Also, check out our case study for five lessons learned to accelerate successful impact measurement as an investor or investee. And if you enjoyed this post, share it, tweet it, or comment below! We’re also very curious about what social + business metric combinations have or haven’tworked for you. We look forward to hearing from you.
See? Impact measurement isn’t as scary (or as boring) as it may first seem.
Rebecca Baylor is a research associate for the Performance Measurement Initiative.
Heather Esper is the senior program manager for WDI’s Performance Measurement Initiative.
Yaquta Kanchwala Fatehi is a program manager for WDI’s Performance Measurement Initiative.

Many organizations working with small businesses in low-income countries struggle with how to separate powerful, but anecdotal, stories from true social impact that can be replicated.
The newly released WDI Impact Report, “Positive Change Through Actionable Metrics,” reviews the work of the Institute’s Performance Measurement Initiative (PMI) while pilot-testing a new framework in Brazil, Nicaragua and Peru designed to increase the impact of small, inclusive businesses and their distribution networks.
The latest report traces WDI’s work back to a 2015 Mexico conference sponsored by the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) where WDI Senior Program Manager Heather Esper debuted the new framework, which includes a mix of standardized social and business metrics over the short and long term. There was great interest in having WDI pilot the framework with different micro-distribution organizations in IDB’s SCALA network, which brings together anchor companies, microfinance institutions, academia and non-governmental organizations to combine efforts to grow inclusive distribution networks.
Three SCALA network organizations were selected – Supply Hope in Nicaragua, Chakipi Acceso in Peru and Kiteiras in Brazil – and WDI went to work to identify indicators from the framework that would properly reflect the impact on the micro-distributors for each venture. The team also developed context-specific collection plans for gathering the necessary data. This helped the enterprises increase their data collection skills, and allowed WDI to test how much practical guidance future organizations would need if they were using the framework.
 “We are pleased to release this impact report that highlights our work with three great organizations to achieve measurement that is actually meaningful to them,” said WDI Research Associate Rebecca Baylor. “The teams we worked with deserve a lot of credit for the success of this project. So many organizations are struggling with how to measure their impacts, and these teams were willing to have in-depth conversations and reflect on their data collection practices.”
“We are pleased to release this impact report that highlights our work with three great organizations to achieve measurement that is actually meaningful to them,” said WDI Research Associate Rebecca Baylor. “The teams we worked with deserve a lot of credit for the success of this project. So many organizations are struggling with how to measure their impacts, and these teams were willing to have in-depth conversations and reflect on their data collection practices.”
As the report chronicles, WDI developed surveys for the three organizations and helped them collect and analyze the data. The work culminated in a set of recommendations for the three organizations to apply in future impact measurement activities. All three gained a better understanding of how to measure changes in the well-being of their micro-distributors.
“They were committed to building their capacity for making decisions with the data they collect,” Baylor said. “This report shares the process we went through together and will be valuable for other organizations who are striving to accomplish the same.”
It’s the second report in an ongoing series that chronicle the long-term impact WDI is having in certain sectors or geographies. The first WDI Impact Report, “Improving Business Education in the Philippines,” debuted in March 2017. It examined the Institute’s contributions to the five-year STRIDE project that focused on strengthening the science, technology, research and innovation capacity on the island nation.

BA685 students working with Ethio-American Doctors Group (EADG) in Ethiopia interview a physician.
Qin Dong said the healthcare delivery course she took this semester taught her a lot about practices inside and outside the United States, including how healthcare organizations harnessed different business models to scale up and meet patient needs.But the biggest lesson for Dong from the weeks of classroom learning and in-country work came down to empathizing with the customer.
“My takeaway is probably true for every consulting-like project: don’t make assumptions about what is best for the customers, listen to them, and cater to their needs,” she said. “Any recommendations that don’t fit with a customer’s situation won’t be helpful at all regardless how successful it was in the past.”
Dong’s Rwanda team was one of five that spread out around the globe for the BA685: Healthcare Delivery in Emerging Markets course taught by WDI President Paul Clyde. Other teams worked in Ethiopia, India, Peru and Sri Lanka. All five teams will present recaps of their projects at 5 p.m. on April 16 in Room R1240 at the University of Michigan’s Ross School of Business. It is free and open to the public, and students in business, public health and other disciplines are encouraged to attend. A reception will follow.
Comprised mostly of MBA2 students, the course is designed to enhance participants’ international leadership capabilities, increase awareness of diverse business issues within the current global landscape, provide on-the-ground experience in a foreign country, and contribute to the success of partner health clinics and hospitals.
The course, organized and primarily funded by WDI with some financial support from Ross, responds to the increasing need for managers to have an international business perspective to augment their business and management knowledge. During the first part of the term, students learned about healthcare in emerging markets through lectures, guest speakers and case discussions. Students were then divided into five teams and prepared for visits to their selected country, traveling to those destinations in late February and early March.
The travel-study course empowers students to integrate what they learned in the classroom with hands-on experience. But unlike the Ross School Multidisciplinary Action Projects (MAP), Dong said the healthcare delivery course “exposes us to an environment where sponsors and other stakeholders have little business knowledge and no clear expectations about the projects.
“This can increase the difficulty and scope of the projects. However, it mimics real-life situations for the most part,” she said.
Clyde said the course is “business education at its best” – a collaborative learning environment with faculty and students learning from each other in an action-based learning setting.
“This course allows me to have detailed conversations with the students about some of the newer approaches to healthcare in low- and middle-income countries, and then gives them the chance to experience some of those markets in person and develop some of these new methods in concert with the institution,” Clyde said. “No matter how much I discuss it in class, there is no way to convey all of the challenges and opportunities in these markets without having the students actually visit the locations.”
Jennie Proto Gondhi, who was part of the Sri Lanka team, said she was attracted to the class to learn about the business perspective of healthcare and how business models can help solve public health problems. In pursuing a dual master’s in public health in epidemiology as well as health education/health behavior, Proto Gondhi said her classes dig deeply into evidence-based programs and validating data.
“However, I think sometimes a missing piece to public health problem solving is the idea that revenue, marketing and market value keeps programming going,” Proto Gondhi said.
She said the course showed her how valuable it is for people with public health and business skill sets to work in tandem to make a program successful.
“I enjoyed working and deliberating with teammates with varied expertise,” she said. “As we get ready to prepare our final reports and presentations, I walk away with the idea that public health programming can only be enhanced with further collaboration.”
Ross MBA student Kevin Jones, who worked with his team in Peru, called the course “probably the best interdisciplinary experience I’ve had at U-M.
“It integrates communities from the business, public health, policy and medical schools who have different but relevant perspectives on how to approach problems,” he said.
The Peru team worked with the Peruvian American Medical Society, a first-time partner for the course. The other institutions – Ethio-American Doctors Group (Ethiopia), LiveWell (India), Ruli District Hospital (Rwanda) and Grace Care Center (Sri Lanka) – have participated in the course multiple times, which allows Ross and WDI to build deep relationships and trust. Repeat partners also provides WDI with insights on what has and hasn’t worked with each institution, and that information is brought to bear in each project.
Here is a summary of each partner and project.
TEAM: Ethio-American Doctors Group (EADG)
LOCATION: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
BACKGROUND: The Ethio-American Doctors Group is comprised of over 250 U.S. physicians of Ethiopian descent who have committed time and money to establish a state-of-the-art tertiary care hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
PROJECT FOCUS: Develop a business model for a program to train nurses to international standards.
TEAM: Grace Care Center (GCC)
LOCATION: Trincomalee & Colombo, Sri Lanka
BACKGROUND: There is an extreme shortage of physicians in Sri Lanka and the number of people needing diabetes treatment is growing, making the shortage more acute. A GCC project looks into adding a new category of healthcare providers – diabetes technicians – to address the need.
PROJECT FOCUS: Assess the viability of a diabetic technician training program and undertake a market analysis to develop an understanding of the potential demand for such skills from existing physicians.
TEAM: LiveWell
LOCATION: Hyderabad, India
BACKGROUND: LiveWell Rehab Center in Madurai, India has been in operation since 2011. In October 2017, LiveWell began operations in Hyderabad.
PROJECT FOCUS: Examine the internal processes of the Hyderabad center compared to the Madurai facility to look for improvements.
TEAM: Peruvian American Medical Society (PAMS)
LOCATION: Chincha, Peru
BACKGROUND: PAMS Policlinico is a clinic offering multiple services, but is looking to become a center of excellence in ophthalmic surgery and gastroenterology.
PROJECT FOCUS: Conduct a market analysis to assess the profitability of a center of excellence in ophthalmic surgery and gastroenterology.
TEAM: Ruli District Hospital
LOCATION: Ruli, Rwanda
BACKGROUND: Ruli District Hospital, about two hours from Kigali, has worked with WDI for seven years and many of the projects are seeing fruit now.
PROJECT FOCUS: Study the revenue generating opportunities of a private clinic within the hospital.